About the program
- Home
- About
The NT POCT Program sits within the Flinders University International Centre for Point-of-Care Testing and is comprised of the i-STAT and WBC DIFF POCT networks.
The NT POCT Team delivers training, support and quality management for these networks and conducts research to evaluate and highlight the clinical, operational effectiveness and outcomes of the Program.
i-STAT POCT
Since it began in 2008, this program has proven time and time again to be operationally effective. The number of patient tests conducted annually has increased ten-fold and qualitative research has demonstrated a high level of satisfaction with the program among a range of stakeholders including doctors, remote area nurses and Aboriginal Health Practitioners.
The i-STAT POCT program is also clinically effective, with particular impact on improving clinical outcomes for cardiac and acutely ill patients. Many remote health staff have commented that the use of the i-STAT has enabled patients to be safely monitored and stabilised on-site and led to improved patient safety in remote communities.
There have been multiple instances of saved medical evacuations due to the ability to conduct on-site POC testing to evaluate the immediate clinical status of patients (with resultant cost savings of approximately $21 million per annum for the Northern Territory Government).
WBC DIFF POCT
White blood cell counts are an important diagnostic tool for detecting acute and general infections, but obtaining reliable test results in a timely manner from pathology laboratories presents significant challenges for remote communities. These challenges include long specimen transport times and issues related to specimen integrity during transport. Our 2017 study found that more than 25% of tests ordered by remote communities were reported by their nearest laboratory as 'unreliable', 'unsuitable' and 'not reported' due to these issues.
In response to this, NT Health and the Flinders University International Centre for Point-of-Care Testing examined the analytical, clinical and cost effectiveness of a POC testing device for total white blood cell counts and their subtypes. In 2020, this study led to the introduction of HemoCue(R) WBC DIFF devices to 20 remote clinics in the Northern Territory's Top End region. The WBC DIFF device generates a total white cell count and a 5-part differential white blood cell count in under 5 minutes.
Based on our research the WBC DIFF POCT program is expected to have significant benefits for Top End communities, including rapid identification and timely treatment of patients with infection/sepsis, more effective triage of patients who require evacuation (by making informed clinical decisions on-site as a result of access to POC testing), and cost savings due to prevented medical evacuations.
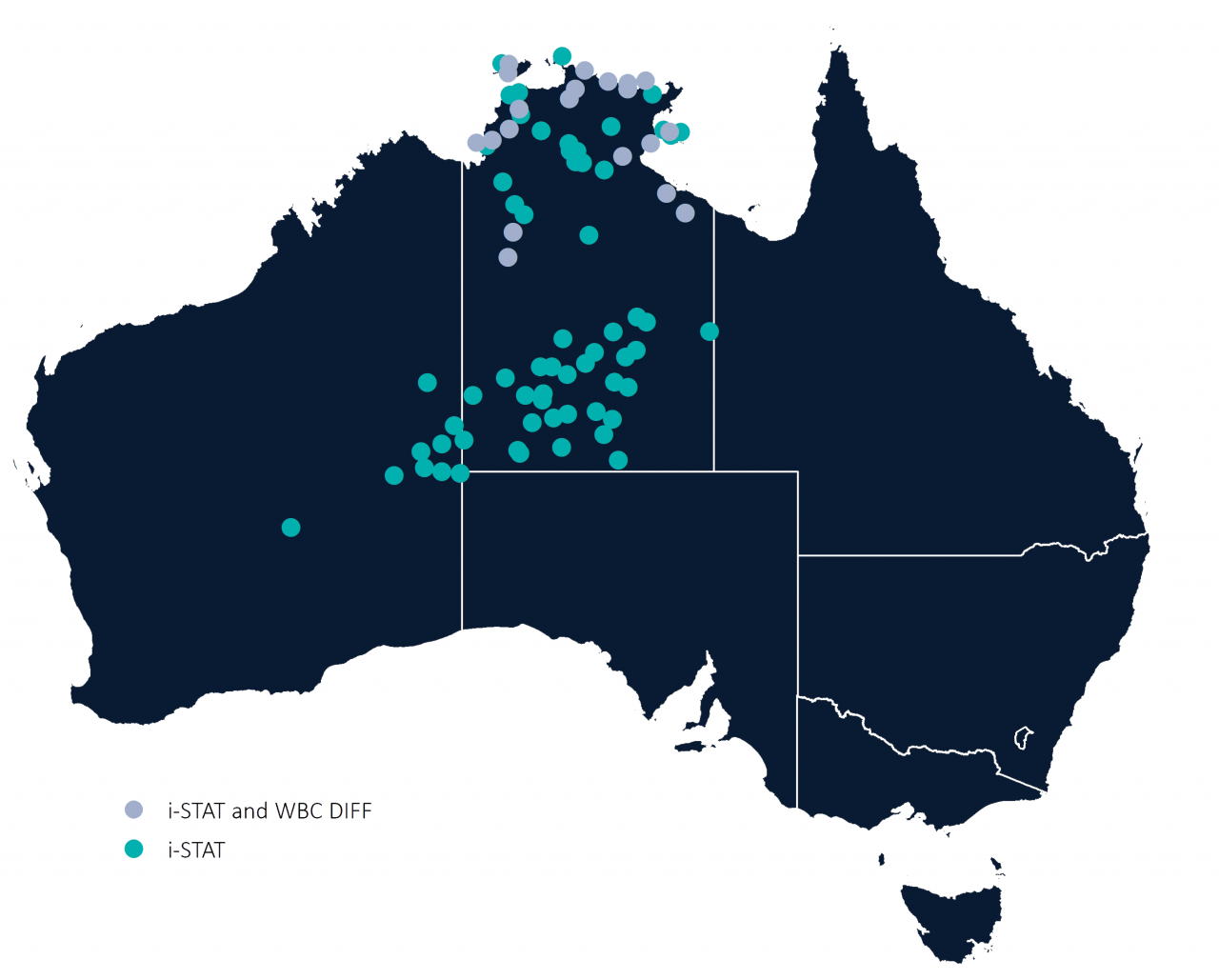
Where are we active?
Funding partner
The NT POCT Program is funded by the Northern Territory Government.
